Effective Ways to Understand Keto Enol Tautomerism in Modern Chemistry
Introduction to Keto Enol Tautomerism
Keto enol tautomerism is a significant topic in organic chemistry, marking the dynamic equilibrium between two structural isomers: the **keto form** and the **enol form**. This concept, known as tautomeric equilibrium, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and reactivity patterns within carbonyl compounds, such as **aldehyde ketones**. Understanding keto enol tautomerism is essential for chemists as it impacts synthetic strategies and reaction mechanisms involved in organic synthesis.
The Basics of Tautomerization
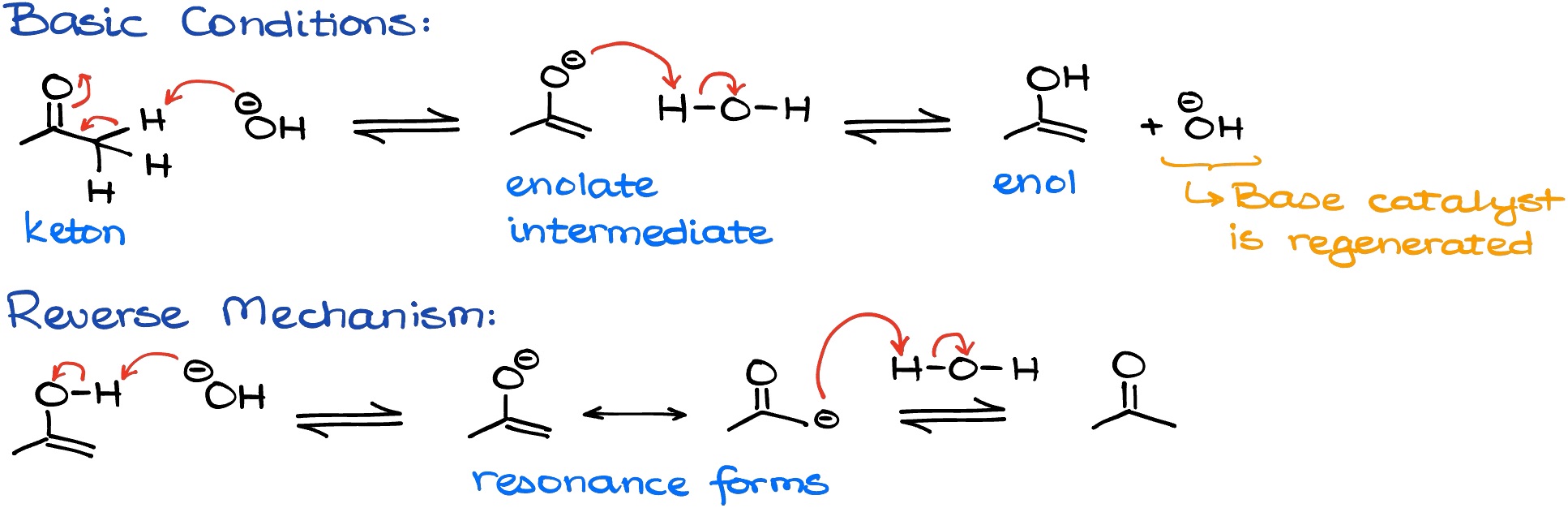
Tautomerization refers to the process of **keto-enol tautomerization**, where a hydrogen atom shifts between two adjacent atoms, altering the molecular structure. In simpler terms, it is a type of **structural isomerism**. The **keto form** typically features a carbonyl group, while the **enol form** has a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond. This **reaction mechanism** can be impacted by various factors, including solvent effects and acid-base catalysis. For instance, acidic conditions generally favor the formation of the keto form, while basic conditions enhance the stability of the enolate ion, which is an essential species in many organic transformations.
Illustrating Keto Enol Tautomerism with Examples
To further elucidate this concept, consider the example of acetylacetone. Under equilibrium conditions, this compound exhibits keto-enol tautomerism. The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the enol form creates stability, altering the tautomer’s **reactivity** and **thermodynamics**. Such examples demonstrate the real-world implications of keto enol tautomerism in organics, emphasizing the necessity for chemists to master these transformations to enhance their understanding of reaction pathways.
Significance of Tautomeric Equilibrium
The relevance of tautomeric equilibrium in modern chemistry cannot be overemphasized. It impacts reactivity in **substitution reactions**, hydrolysis, and **condensation reactions**. Understanding the equilibria involved enables chemists to rationalize reaction outcomes and optimize yields.
The stability of the tautomers can be greatly affected by external factors such as temperature, which influences **reaction rates** and the ratio of keto-enol forms in solution. Additionally, the ability to control the tautomeric forms opens new avenues for manipulation in **synthetic applications**. For example, the enol form of a compound might exhibit unique **functional group chemistry** that can be harnessed for specific transformations in organic synthesis.
Factors Affecting Tautomeric Equilibrium
Several factors influence the keto-enol tautomeric equilibrium, including **acid catalysis** and **base catalysis**. The strength of an acid or base can greatly dictate the predominance of one tautomer over the other. In practice, stronger acids can facilitate the formation of the keto form by more effectively stabilizing the carbonyl group through resonance. Conversely, bases can favor the enol form by promoting the deprotonation that leads to enolate formation
Spectroscopic analysis, particularly **NMR spectroscopy**, also plays a pivotal role in determining the keto/enol ratio in a mixture. By measuring the **chemical shifts** in spectra, chemists can deduce the stability of the individual tautomers based on their environments and interactions.
Applications in Organic Synthesis
Keto enol tautomerism has extensive implications in **organic synthesis**. Its versatility is particularly evident in the contexts of medicinal chemistry and pharmacology, where specific tautomeric forms may possess distinct biological activities. The understanding of **tautomerization reactions** allows chemists to develop strategies for synthesizing complex molecules that require specific configurations of functional groups.
Reaction Mechanisms Involving Keto Enol Tautomerism
Understanding the reaction mechanisms associated with keto enol tautomerism enriches our awareness of organic reactions. These mechanisms often encompass intricate **reaction pathways**, involving intermediates like enolates that considerably influence chemical synthesis. Comprehending the **bond formation** and **bond cleavage** that occurs during tautomerization is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes and designing more effective synthetic routes.
Case Study: Tautomerization in Action
One notable example is the dehydrohalogenation reaction often seen in alkyl halides, where the formation of an enolate is a key step. After deprotonation by a base, the resulting enolate can engage in diverse **nucleophilic attacks**, leading to the formation of stable molecules. Observing how tautomeric species participate in such reactions offers insights into the **kinetic** vs. **thermodynamic control** of the products formed.
Thermodynamic Considerations
When considering keto enol tautomerism, **thermodynamic stability** becomes a central theme. Tautomerization is generally considered a **reversible reaction**, further dictated by the **equilibrium constant**. The position of equilibrium varies between different tautomers, influenced by factors such as substituent effects and steric hindrance.
As temperatures change, reaction rates shift accordingly, evidencing the dynamic nature of tautomerization through experimental data. Understanding how temperature influences keto-enol equilibrium is crucial for optimizing specific reactions within the lab.
Conclusion
In closing, keto enol tautomerism represents a pivotal concept deeply embedded in organic chemistry and vital for interpreting various chemical behaviors and reactions. Mastery of **tautomeric behavior**, the interactive balance between the **keto form**, and the **enol form** significantly enriches our understanding of organic synthesis, reactivity, and molecular interactions. As research advances, the implications of keto enol tautomerism will continue to impact various fields, including pharmaceuticals and materials science, solidifying its importance in both theoretical and practical chemistry.
FAQ
1. What is the fundamental principle behind keto enol tautomerism?
The fundamental principle behind keto enol tautomerism is the reversible interconversion between the **keto form** and the **enol form** of a compound. This involves the movement of a proton (hydrogen atom) between two atoms, changing the structure while maintaining the molecular formula. Understanding this principle is critical for studying the dynamics of organic reactions.
2. How does solvent affect keto enol tautomerization?
Solvent effects play a significant role in keto enol tautomerization by influencing the **stability** of each tautomer. Polar protic solvents can stabilize the **enol form**, while non-polar solvents may favor the **keto form**. This distinction is crucial for optimizing reaction conditions in organic synthesis.
3. Why is understanding tautomer stability important?
Understanding tautomer stability is imperative because it determines which form prevails under specific reaction conditions. Stability is influenced by factors such as hydrogen bonding, steric hindrance, and electronic effects. This knowledge helps chemists predict behavior in chemical transformations and optimize synthetic pathways.
4. Can keto enol tautomerization impact drug design?
Absolutely! The different tautomeric forms can exhibit varying biological activities, which is crucial in drug design. Knowledge of tautomerization allows medicinal chemists to select or modify compounds to achieve desired functionalities and improve therapeutic outcomes.
5. What are some key experimental techniques for studying keto enol tautomerism?
Several experimental techniques are employed to study keto enol tautomerism, including **NMR spectroscopy**, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry. These methods help determine the equilibrium between tautomers, revealing insights into their chemical properties and reactivities.